Chemistry is full of surprises. One minute, you’re juggling numbers; the next, you’re sketching little dots and lines that unlock the secrets of the universe. Today, let’s dive deep into something genuinely intriguing: the CN- Lewis structure. What makes this tiny cyanide ion so captivating? How does it work? Why should you care? Buckle up because we’re about to explore every nook and cranny of this molecular marvel in a way that’s fun, engaging, and—dare I say—mind-blowing!
Table of Biography for “CN- Lewis Structure“
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Cyanide Ion Lewis Structure (CN- Lewis Structure) |
| Composition | One carbon (C) atom and one nitrogen (N) atom |
| Charge | Negative (-1), due to an extra electron |
| Valence Electrons | 10 total (Carbon: 4, Nitrogen: 5, Extra from charge: 1) |
| Bond Type | Triple bond between carbon and nitrogen |
| Lone Pairs | One lone pair on nitrogen |
| Octet Rule | Satisfied for both atoms (8 electrons each via triple bond and lone pair) |
| Toxicity | Highly poisonous; disrupts cellular respiration |
| Importance | Reveals electron distribution and bonding; key in understanding cyanide’s chemical behavior |
| Applications | Used in studying reactions, gold extraction, and organic synthesis |
| Discovery Context | Rooted in Lewis dot theory by Gilbert N. Lewis, developed in early 20th century |
| Environmental Impact | Linked to industrial pollution (e.g., mining), but understanding aids eco-friendly solutions |
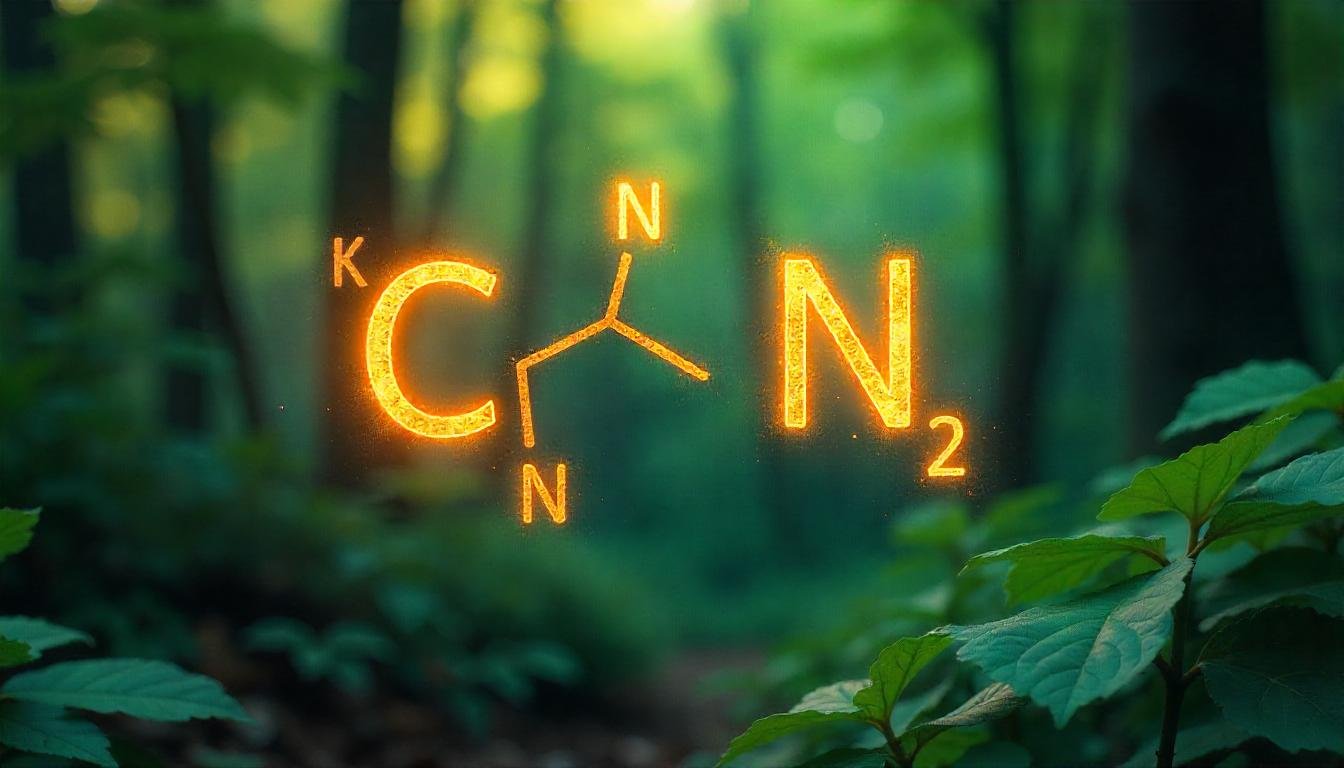
| Visual Representation | Diagram with C≡N, lone pair on N, and brackets with a minus sign: [C≡N]⁻ |
| Fun Fact | Its triple bond is so strong, it’s like carbon and nitrogen are glued together! |
What Exactly Is the CN- Lewis Structure?
Picture this: a carbon atom and a nitrogen atom walk into a bar, and they decide to stick together with a negative charge tagging along. That’s the cyanide ion, or CN-, in a nutshell! The CN- Lewis structure is a diagram that shows how these two atoms bond and where their electrons hang out. Chemists use these sketches to visualize the invisible world of molecules and ions. So, what’s the big deal with CN-? It’s a negatively charged ion with an extra electron up its sleeve, and that little detail changes everything.
Let’s break it down. Carbon brings four valence electrons to the party, nitrogen shows up with 5, and that negative charge tosses in 1 more. Add them up, and you get 10 valence electrons to play with. If you’re drawing the CN- Lewis structure—your job is to arrange those electrons so both atoms feel happy and stable. Spoiler alert: they share much more than you might expect!
How Do You Build the CN- Lewis Structure?
Ready to get your hands dirty? Let’s sketch the CN- Lewis structure step by step. First, place carbon and nitrogen side by side. Why? Because they’re the only two atoms in this ion, and they’re itching to bond. Next, connect them with a single line. That line represents a pair of shared electrons—a single bond. But it gets juicy here: a single bond won’t cut it.
Count the electrons. Carbon shares 2 electrons with nitrogen with a single bond, leaving it with six total (4 of its own plus two shared). Nitrogen, meanwhile, has 7 (5 of its own plus two shared). Neither hits the magic number 8, which the octet rule demands. Atoms love having 8 electrons around them—it’s like their comfort zone. So, what’s the fix? Upgrade that single bond to a triple bond!
Draw three lines between carbon and nitrogen. Now, they share 6 electrons. Carbon ends up with 8 (4 lone plus six shared), and nitrogen gets eight (2 lone plus six shared). Perfect. Almost. Don’t forget that extra electron from the negative charge. Place a lone pair on nitrogen and slap brackets around the whole thing with a minus sign outside. Voilà! You’ve got the CN- Lewis structure: a triple bond, a lone pair, and a negative charge, all wrapped up in one tidy package.
Why Does the Triple Bond in the CN- Lewis Structure Matter?
Let’s zoom in on that triple bond. Three lines between carbon and nitrogen? That’s not just fancy artwork—it’s a powerhouse! Triple bonds are powerful, which explains why cyanide sticks together so tightly. Carbon and nitrogen cling to each other like best friends who refuse to let go. This strength shapes CN- behaves in the wild, whether reacting with different chemicals or sneaking into places it shouldn’t—like your body, where it’s notoriously toxic.
That triple bond also tells us something remarkable about electron sharing. Carbon and nitrogen pool their resources to hit that octet sweet spot. It’s teamwork at its finest! But here’s a question: why doesn’t carbon take the lone pair instead of nitrogen? Good thought! Nitrogen is more electronegative—it loves electrons more than carbon does. So, it hogs that lone pair, leaving carbon content with just the shared electrons. The CN- Lewis structure reveals this tug-of-war in action.
Is the CN- Lewis Structure Dangerous?
Let’s get real for a second. Cyanide isn’t just a chemistry puzzle—it’s a poison! The CN- Lewis structure helps us understand why it’s so deadly. That negative charge makes CN- super reactive. It latches onto enzymes in your body, like cytochrome c oxidase, and shuts down your cells’ ability to use oxygen. No oxygen, no energy, no life. Yikes! The triple bond’s stability keeps CN- intact long enough to wreak havoc, which is why chemists handle it with kid gloves.
But don’t panic—studying the CN- Lewis structure won’t hurt you! It’s a safe way to peek at something dangerous from a distance. Think of it like watching a lion through a zoo’s glass wall: fascinating, but you’re in no danger.
What Makes the CN- Lewis Structure So Useful?
Why bother with all these dots and lines? The CN- Lewis structure isn’t just a pretty picture—it’s a roadmap. Chemists use it to predict how CN- will act in reactions. Will it bond with a metal? Donate electrons? Steal them? The structure holds the clues. That negative charge, for instance, hints that CN- might cozy up to positively charged ions. The triple bond suggests it’s tough to break apart. Put those together, and you’ve got a recipe for understanding cyanide’s role in everything from gold mining to organic synthesis.
Plus, it’s a brain workout! Figuring out the CN- Lewis structure sharpens your skills for tackling trickier molecules. It’s like a warm-up lap before the big race. Once you nail this, you’ll feel ready to sketch anything chemistry throws your way.
Can the CN- Lewis Structure Teach Us About Sustainability?
Here’s a twist: the CN- Lewis structure even ties into eco-friendly ideas! Cyanide appears in industrial processes like gold extraction, but its toxicity poses environmental risks. Understanding its structure helps scientists design safer alternatives or clean-up methods. Imagine a world where we use chemistry knowledge to protect nature instead of harming it—that’s the thinking the CN- Lewis structure inspires. Who knew a tiny ion could spark big ideas?
How Does the CN- Lewis Structure Compare to Other Ions?
Let’s play a little game of “spot the difference.” Take CO and carbon monoxide. It’s neutral, not an ion, and has a triple bond too. But unlike CN-, it lacks that extra electron, so its behavior shifts. Or consider OH-, the hydroxide ion. It’s got a single bond and a negative charge, but it’s nowhere near as toxic. The CN- Lewis structure stands out with its unique combo of a triple bond and a negative charge, making it a bit of a rebel in the ion world. Comparing these structures is like flipping through a chemistry family album—each has its personality!
What’s the Funniest Thing About the CN- Lewis Structure?
Okay, let’s lighten things up. Ever think about how carbon and nitrogen sound like a comedy duo? Carbon’s all, “I’ve got 4 electrons to share!” and nitrogen chimes in, “Well, I’ve got 5, plus this extra one I stole!” Together, they juggle 10 electrons, tossing them back and forth until they land that triple bond. The CN- Lewis structure is their punchline—a perfectly balanced act with a twist of danger. It’s chemistry’s version of a buddy cop movie: two atoms, one wild adventure!

Why Should You Keep Exploring the CN- Lewis Structure?
Here’s the kicker: the CN- Lewis structure is just the beginning. It opens doors to more significant questions. How do electrons shape the world? What makes some bonds unbreakable? Why do tiny ions have such huge impacts? Every time you sketch it, you’re not just drawing but uncovering a story. So, grab a pencil, try it, and see where it takes you. Who knows? You might fall in love with the quirky, dangerous, brilliant world of cyanide chemistry.
There you have it—a whirlwind tour of the CN- Lewis structure! From its triple-bonded heart to its toxic reputation, this little ion packs a punch. What do you think? Are you ready to tackle it yourself? Let’s hear your thoughts!